What is a Forex Calendar?
Forex Calendar - When studying forex, you may often hear the word Forex Calendar. What is Forex Calendar? What's the difference from an ordinary calendar that hangs in your living room?
Forex Calendar is a term for a calendar used by traders and investors to monitor events that have the potential to move the financial market.
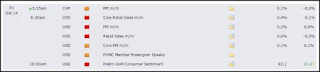
A Forex Calendar is usually displayed in the form of tables per specific date where each day contains several market driving events in chronological order. The potential impact that will emerge from each event is also displayed in the Forex Calendar in the form of certain symbols or colors, making it easier for traders and user investors to anticipate the possible consequences of these events.
Perhaps it is rather difficult to imagine by lay people who have never been in the financial market as traders or investors, but is the fact that the announcement of some economic data and policies can spontaneously have a huge impact. Some examples of the impact are increasing or decreasing the exchange rate of a country's currency, increasing or dropping stock prices, and so on.
The data whose announcement date is published by the Forex Calendar is more familiarly called economic indicators, namely statistical data that show certain information about economic conditions / activities in a country or region in a certain period. Economic indicators are usually released by government agencies, international organizations, or private research institutions. For example, every quarter (quarterly) the United States Government releases data on Gross Domestic Product (Gross Domestic Product / GDP). The data allows investors to analyze the performance of the US economy for the previous three months, and compare the numbers with last year's performance; how well economic performance in GDP can have a significant impact on investment decisions made by market participants.
In addition, the Forex Calendar contains a schedule of meetings and announcements of monetary policy from leading central banks. The central bank acts as a regulator of the circulation of money, while monetary policy is a general rule that becomes a reference in controlling the circulation of money in a country. The central bank holds meetings several times a year to discuss current economic conditions and determine whether monetary policy needs to be changed or not. The meeting will be followed by an announcement / press conference. One example of monetary policy is the increase or decrease in interest rates.
Is it important for forex traders to understand economic indicators and the types of central bank policies? Actually it's not mandatory, but it will be very useful if the trader knows which events can have a big impact on the financial market. By knowing, it can take advantage of the moment if it is potentially profitable, or vice versa, avoid the market at certain times when there is an event that is likely to trigger turmoil.
Each event in the Forex Calendar is usually accompanied by a marker of the level of volatility or the amount of movement in the market that is expected to be triggered by the event. There are three levels of volatility: low (yellow / one bull / one exclamation point), medium (orange / two bulls / two exclamation marks), high (red / three bulls / three exclamation points).
The following are some potentially high impact events in the Forex Calendar that are important to observe:
1. ISM PMI Index.
The ISM (Purchasing Managers Index Institute for Supply Management) PMI index is one of the economic indicators that monitors the climate of the United States manufacturing business sector. The data is released on a 100 and median scale of 50. If a number above 50 means an expansionary economy, if it is below 50 it means it is under pressure.
2. ISM Non-Manufacturing PMI Index.
Similar to point 1, but the Non-Manufacturing ISM PMI index seeks to measure the business climate in other service and non-manufacturing sectors.
3. Empire State Manufacturing Survey.
The Empire State Manufacturing Survey report was made by the Federal Reserve Bank of New York to explore the views of business people about business conditions in the state of New York in general.
4. FED Philadelphia Business Outlook Survey.
The FED Philadelphia Business Outlook Survey is a measure of business climate indicators made by the Federal Reserve Bank of Philadelphia to monitor manufacturing business conditions in the states of Pennsylvania, New Jersey and Delaware. Data has a median of 0. If the index number is above zero, then it means growth (expansion), whereas if the number below zero means contraction (depressed)
5. Gross Domestic Product (GDP).
GDP shows the economic growth rate of a country and is published in a quarterly period by the relevant government. In the United States, GDP data for one period is released three times (preliminary, second estimate, final), but in other countries it is usually only twice (preliminary, final) or just once. The increase in GDP figures compared to previous reporting will have a positive impact on the related currency, whereas if a decline occurs it can be a debilitating factor.
6. Industrial Production Index.
The Industrial Production Index (Industrial Production Index) calculates real production output from manufacturing, mining and other manufacturing sectors such as oil and gas and electricity. This data has a major impact when published by countries with industry as its foundation, such as the United States, because it contributes greatly to economic growth (GDP).
7. United States Consumer Sentiment Index.
The Consumer Sentiment Index published by the University of Michigan Consumer Sentiment Index measures people's views about their own financial conditions and general economic conditions. It is assumed that if people are more optimistic, they will be more willing to spend their money, which can encourage the economy to grow.
8. Orders Durable Goods (Durable Goods Orders)
This data shows the growth in the number of new orders for durable goods made in the United States and provides information about how busy manufacturing companies are in the future. If the percentage of growth is higher than expectations, it will be positive for the US Dollar.
9. Consumer Confidence Index.
High Consumer Trust will be realized in more active saving and shopping activities. Therefore, a survey was conducted to measure the Consumer Trust Index. In the United States, this data is created and reported by the Conference Board (CB).
10. New Home Sales.
New Home Sales includes economic indicators from the housing sector (Housing) and specifically calculates the sale of newly built homes in the United States.
11. Building Permits.
Building Permits are also classified as housing sector economic indicators in the Forex Calendar, but note the development of the number of permits granted by the government or related authorities before the construction of a property can begin in the United States.
12. Existing Home Sales.
Slightly different from New Home Sales, Existing Home Sales calculates the number and price of sales of family homes, condominiums, and apartments whose status has been built in the United States.
13. Housing Starts.
Data on Housing Starts reports on the number of new housing development projects starting in a particular month in the United States. This report is a support for other housing sector data.
14. Personal Expenditures and Income (Personal Income and Outlays).
In the Personal Expenditures and Income report there are indicators of Personal Income, Personal Spending, PCE Index, and Core PCE Index which are the reference materials for the part of the US central bank to take policy. These data also present an initial indication for GDP and inflation.
15. Retail Sales.
Sales reports in the retail trade sector are issued monthly in the form of percentage changes compared to the previous month. This report usually consists of two numbers: Retail Sales and Core Retail Sales. The difference is, the first number includes all goods, while Core Retail Sales excludes sales of automotive goods.
16. Initial Jobless Claims.
In the Forex Calendar, Initial Jobless Claims are the number of applications for new applications or claims submitted by individuals to obtain unemployment benefits in the US. The greater the number, the more negative it will be for the US economic outlook, whereas if there is a decline it will be a positive indication.
17. Current Employment Statistics (Current Employment Statistics)
The most complete current employment conditions data are from the United States. Released in the monthly period, the most important figures in Current Employment Statistics include Nonfarm Payroll (number of new people working in the non-agricultural private sector), unemployment rate, growth rate of average salary, and level of labor participation.
18. Consumer Price Index (CPI).
CPI is an indicator of consumer inflation, indicating an increase or decrease in prices of goods and services continuously at the consumer level for a certain period. There are several inflation gauges other than CPI, such as PPI (Producer Price Index) and Import Prices. But, among other things, CPI inflation had the greatest impact. PPI data releases usually only have a medium impact, while Import Prices have a low impact.
19. Producer Price Index (PPI).
PPI shows changes in output prices that have been produced by producers.
20. Monthly Treasury Statement.
Data released every month by the US Treasury contains a report on the financial activities of the US federal government (budget and expenditure).
21. International Trade.
In the Forex Calendar, there are at least three indicators that are observed in the International Trade report, namely Export, Import, and Trade Balance.
22. Treasury International Capital (TIC).
Treasury International Capital (TIC) is a statistical report that shows all flows of funds in and out of the country in buying and selling financial and securities instruments in the US.
23. TANN.
TANKAN is a quarterly survey of business beliefs held and reported by the Bank of Japan. Data includes material for policy making and is considered capable of providing an accurate picture of business trends in Japan.
24. Ifo Business Climate Index.
The ifo Business Climate Index (ifo Business Climate Index) is an indicator of German economic activity based on a monthly survey conducted and reported by the Ifo Institute. Germany is the largest country in the European region, so this data is a big influence in the Forex Calendar.
25. ZEW Economic Sentiment Index.
The ZEW Economic Sentiment Index (ZEW Economic Index) is an indicator that monitors the views of experts on economic conditions and outlook, especially in Germany and the Eurozone.
26. Announcement of Monetary / Interest Rate Policy.
As explained above, monetary policy taken by leading central banks can have a major impact on the financial market. Among these leading central banks are the Federal Reserve (FED) in the United States, the Bank of England (BoE), the European Central Bank (ECB), the Bank of Japan (BoJ), the Reserve Bank of Australia (Reserve), the Reserve Bank of New Zealand (RBNZ), Bank of Canada (BoC), and Swiss National Bank (SNB). Schedule of meetings and policy announcements can be seen on the site of the central banks as well as on the Forex Calendar.
It is worth noting that economic indicators are usually released by government agencies, international organizations, or private research institutions throughout the world. Therefore, it will be difficult if you want to track it yourself one by one. For this reason, the existence of the Forex Calendar is very helpful for investors. Already many forex brokers provide Forex Calendar to be accessed freely on their website or in an integrated trading software provided. Also, many websites provide Forex Calendar for free.
Understanding of Forex Calendar
Forex Calendar is a term for a calendar used by traders and investors to monitor events that have the potential to move the financial market.
A Forex Calendar is usually displayed in the form of tables per specific date where each day contains several market driving events in chronological order. The potential impact that will emerge from each event is also displayed in the Forex Calendar in the form of certain symbols or colors, making it easier for traders and user investors to anticipate the possible consequences of these events.
Perhaps it is rather difficult to imagine by lay people who have never been in the financial market as traders or investors, but is the fact that the announcement of some economic data and policies can spontaneously have a huge impact. Some examples of the impact are increasing or decreasing the exchange rate of a country's currency, increasing or dropping stock prices, and so on.
The data whose announcement date is published by the Forex Calendar is more familiarly called economic indicators, namely statistical data that show certain information about economic conditions / activities in a country or region in a certain period. Economic indicators are usually released by government agencies, international organizations, or private research institutions. For example, every quarter (quarterly) the United States Government releases data on Gross Domestic Product (Gross Domestic Product / GDP). The data allows investors to analyze the performance of the US economy for the previous three months, and compare the numbers with last year's performance; how well economic performance in GDP can have a significant impact on investment decisions made by market participants.
In addition, the Forex Calendar contains a schedule of meetings and announcements of monetary policy from leading central banks. The central bank acts as a regulator of the circulation of money, while monetary policy is a general rule that becomes a reference in controlling the circulation of money in a country. The central bank holds meetings several times a year to discuss current economic conditions and determine whether monetary policy needs to be changed or not. The meeting will be followed by an announcement / press conference. One example of monetary policy is the increase or decrease in interest rates.
Is it important for forex traders to understand economic indicators and the types of central bank policies? Actually it's not mandatory, but it will be very useful if the trader knows which events can have a big impact on the financial market. By knowing, it can take advantage of the moment if it is potentially profitable, or vice versa, avoid the market at certain times when there is an event that is likely to trigger turmoil.
Events in the Forex Calendar and the potential impact
Each event in the Forex Calendar is usually accompanied by a marker of the level of volatility or the amount of movement in the market that is expected to be triggered by the event. There are three levels of volatility: low (yellow / one bull / one exclamation point), medium (orange / two bulls / two exclamation marks), high (red / three bulls / three exclamation points).
The following are some potentially high impact events in the Forex Calendar that are important to observe:
1. ISM PMI Index.
The ISM (Purchasing Managers Index Institute for Supply Management) PMI index is one of the economic indicators that monitors the climate of the United States manufacturing business sector. The data is released on a 100 and median scale of 50. If a number above 50 means an expansionary economy, if it is below 50 it means it is under pressure.
2. ISM Non-Manufacturing PMI Index.
Similar to point 1, but the Non-Manufacturing ISM PMI index seeks to measure the business climate in other service and non-manufacturing sectors.
3. Empire State Manufacturing Survey.
The Empire State Manufacturing Survey report was made by the Federal Reserve Bank of New York to explore the views of business people about business conditions in the state of New York in general.
4. FED Philadelphia Business Outlook Survey.
The FED Philadelphia Business Outlook Survey is a measure of business climate indicators made by the Federal Reserve Bank of Philadelphia to monitor manufacturing business conditions in the states of Pennsylvania, New Jersey and Delaware. Data has a median of 0. If the index number is above zero, then it means growth (expansion), whereas if the number below zero means contraction (depressed)
5. Gross Domestic Product (GDP).
GDP shows the economic growth rate of a country and is published in a quarterly period by the relevant government. In the United States, GDP data for one period is released three times (preliminary, second estimate, final), but in other countries it is usually only twice (preliminary, final) or just once. The increase in GDP figures compared to previous reporting will have a positive impact on the related currency, whereas if a decline occurs it can be a debilitating factor.
6. Industrial Production Index.
The Industrial Production Index (Industrial Production Index) calculates real production output from manufacturing, mining and other manufacturing sectors such as oil and gas and electricity. This data has a major impact when published by countries with industry as its foundation, such as the United States, because it contributes greatly to economic growth (GDP).
7. United States Consumer Sentiment Index.
The Consumer Sentiment Index published by the University of Michigan Consumer Sentiment Index measures people's views about their own financial conditions and general economic conditions. It is assumed that if people are more optimistic, they will be more willing to spend their money, which can encourage the economy to grow.
8. Orders Durable Goods (Durable Goods Orders)
This data shows the growth in the number of new orders for durable goods made in the United States and provides information about how busy manufacturing companies are in the future. If the percentage of growth is higher than expectations, it will be positive for the US Dollar.
9. Consumer Confidence Index.
High Consumer Trust will be realized in more active saving and shopping activities. Therefore, a survey was conducted to measure the Consumer Trust Index. In the United States, this data is created and reported by the Conference Board (CB).
10. New Home Sales.
New Home Sales includes economic indicators from the housing sector (Housing) and specifically calculates the sale of newly built homes in the United States.
11. Building Permits.
Building Permits are also classified as housing sector economic indicators in the Forex Calendar, but note the development of the number of permits granted by the government or related authorities before the construction of a property can begin in the United States.
12. Existing Home Sales.
Slightly different from New Home Sales, Existing Home Sales calculates the number and price of sales of family homes, condominiums, and apartments whose status has been built in the United States.
13. Housing Starts.
Data on Housing Starts reports on the number of new housing development projects starting in a particular month in the United States. This report is a support for other housing sector data.
14. Personal Expenditures and Income (Personal Income and Outlays).
In the Personal Expenditures and Income report there are indicators of Personal Income, Personal Spending, PCE Index, and Core PCE Index which are the reference materials for the part of the US central bank to take policy. These data also present an initial indication for GDP and inflation.
15. Retail Sales.
Sales reports in the retail trade sector are issued monthly in the form of percentage changes compared to the previous month. This report usually consists of two numbers: Retail Sales and Core Retail Sales. The difference is, the first number includes all goods, while Core Retail Sales excludes sales of automotive goods.
16. Initial Jobless Claims.
In the Forex Calendar, Initial Jobless Claims are the number of applications for new applications or claims submitted by individuals to obtain unemployment benefits in the US. The greater the number, the more negative it will be for the US economic outlook, whereas if there is a decline it will be a positive indication.
17. Current Employment Statistics (Current Employment Statistics)
The most complete current employment conditions data are from the United States. Released in the monthly period, the most important figures in Current Employment Statistics include Nonfarm Payroll (number of new people working in the non-agricultural private sector), unemployment rate, growth rate of average salary, and level of labor participation.
18. Consumer Price Index (CPI).
CPI is an indicator of consumer inflation, indicating an increase or decrease in prices of goods and services continuously at the consumer level for a certain period. There are several inflation gauges other than CPI, such as PPI (Producer Price Index) and Import Prices. But, among other things, CPI inflation had the greatest impact. PPI data releases usually only have a medium impact, while Import Prices have a low impact.
19. Producer Price Index (PPI).
PPI shows changes in output prices that have been produced by producers.
20. Monthly Treasury Statement.
Data released every month by the US Treasury contains a report on the financial activities of the US federal government (budget and expenditure).
21. International Trade.
In the Forex Calendar, there are at least three indicators that are observed in the International Trade report, namely Export, Import, and Trade Balance.
22. Treasury International Capital (TIC).
Treasury International Capital (TIC) is a statistical report that shows all flows of funds in and out of the country in buying and selling financial and securities instruments in the US.
23. TANN.
TANKAN is a quarterly survey of business beliefs held and reported by the Bank of Japan. Data includes material for policy making and is considered capable of providing an accurate picture of business trends in Japan.
24. Ifo Business Climate Index.
The ifo Business Climate Index (ifo Business Climate Index) is an indicator of German economic activity based on a monthly survey conducted and reported by the Ifo Institute. Germany is the largest country in the European region, so this data is a big influence in the Forex Calendar.
25. ZEW Economic Sentiment Index.
The ZEW Economic Sentiment Index (ZEW Economic Index) is an indicator that monitors the views of experts on economic conditions and outlook, especially in Germany and the Eurozone.
26. Announcement of Monetary / Interest Rate Policy.
As explained above, monetary policy taken by leading central banks can have a major impact on the financial market. Among these leading central banks are the Federal Reserve (FED) in the United States, the Bank of England (BoE), the European Central Bank (ECB), the Bank of Japan (BoJ), the Reserve Bank of Australia (Reserve), the Reserve Bank of New Zealand (RBNZ), Bank of Canada (BoC), and Swiss National Bank (SNB). Schedule of meetings and policy announcements can be seen on the site of the central banks as well as on the Forex Calendar.
It is worth noting that economic indicators are usually released by government agencies, international organizations, or private research institutions throughout the world. Therefore, it will be difficult if you want to track it yourself one by one. For this reason, the existence of the Forex Calendar is very helpful for investors. Already many forex brokers provide Forex Calendar to be accessed freely on their website or in an integrated trading software provided. Also, many websites provide Forex Calendar for free.

Post a Comment for "What is a Forex Calendar?"
Provide comments relevant to the posted articles and provide critiques and suggestions for the progress of the blog